
Investigation & Response Division
MAIN FUNCTION
Conduct regulatory investigation and response on work related incidents or accidents, and radiation related matters as per Workplace Safety and Health Act, Chapter 277 and Radiation Protection Act, Chapter 228.
REGULATORY INVESTIGATION (CORE FUNCTION)
SHENA’s Investigation and Response Division (IRD) is mandated to enforce the Workplace Safety and Health Act, Chapter 277 (WSHA) and the Radiation Protection Act, Chapter 228 (RPA) by conducting investigation and response on reported work-related incidents and radiation matters. Investigation covers gathering of evidence to prove of any breach of the provisions under the WSHO and RPA. In the instance, where there is without reasonable doubt and belief that the Individual, Employer, Occupier, Principal or Duty Holder has by his actions or lack of actions or safety and health measures that breached the laws of the country, SHENA shall work closely with Attorney General’s Chambers (AGC) to recommend that the legal process for further outcomes.
In the event that an Individual, Employer, Occupier, Principal or Duty Holder is found to be in breach of the legislation, SHENA has other legal instruments that shall or may be applied to ascertain the factuality of investigation findings supported with evidence and relevant documentation. In line with SHENA Act, Chapter 227, Workplace Safety and Health Act, Chapter 277, and Radiation Protection Act, Chapter 228, SHENA may impose a Stop Work Order (SWO) or a Remedial Order (RO).
Purpose of regulatory investigation
To prevent recurrence.
To identify learnings; and
Where appropriate, to seek the truth and prosecute cases where laws have not been complied with.
Incident that requires investigation
Work-related accident leading to a Fatality
Accident leading to Serious Injury
Dangerous Occurrence
Occupational Diseases
Major Accident in the Control of Major Accident Hazard (COMAH) Facilities
WORKPLACE INITIAL INCIDENT NOTIFICATION & REPORTING REQUIREMENT
Under the Workplace Safety and Health (Incident Reporting) Regulations, 2014, employers, principals/occupiers, licensees, and self-employed workers are required to report:
Accident leading to death
Notification to SHENA as soon as reasonably practicable: Report in writing within 10 days.Dangerous Occurrence (as per Second Schedule of the Workplace Safety and Health Act, Chapter 277)
Notification to SHENA as soon as reasonably practicable: Report in writing within 10 days.Injury with more than 3 consecutive days of sick leave or admitted to hospital for 24 hours or more
Written report within 10 days.Where person subsequently dies after admitted to hospital
Notification to SHENA as soon as reasonably practicable: Report in writing within 10 days.Any accident with hospital treatment
Notification to SHENA as soon as reasonably practicable.Occupational disease (as per Third schedule of the Workplace Safety and Health Act, Chapter 277) Report in writing within 10 days of diagnosis from both Employer and Medical Practitioner.
Major Accident (as per Workplace Safety and Health (Facilities) (COMAH) Regulations, 2013): Duty Holder has the duty to notify and report the major accident to SHENA within SIX (6) hours of the occurrence.
The completed Initial Incident Notification (IIN) shall be submitted to SHENA through the SHENA’s website.
To know more about Incident Reporting, please refer to Report an Incident
WHO NEEDS TO REPORT WORKPLACE INCIDENCES?

TYPES OF REPORTABLE INCIDENTS

DANGEROUS OCCURENCES
SECOND SCHEDULE OF WORKPLACE SAFETY AND HEALTH ACT, CHAPTER 277
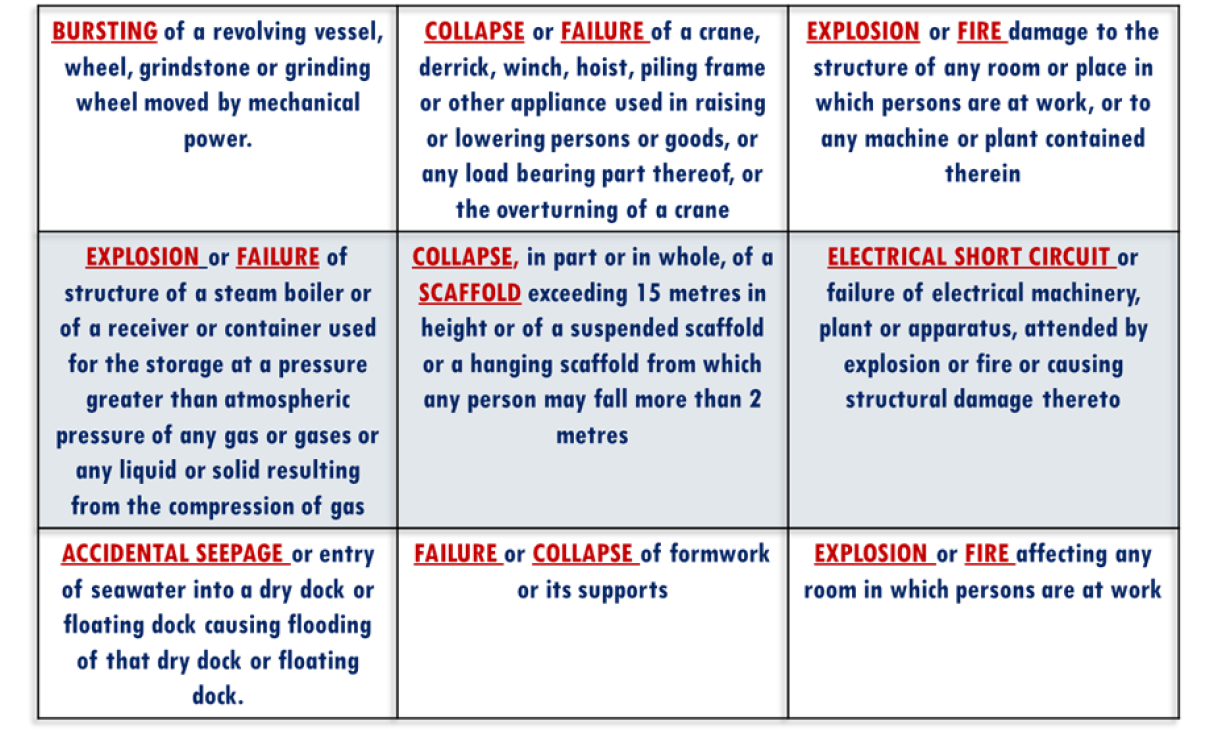
OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES
THIRD SCHEDULE OF WORKPLACE SAFETY AND HEALTH ACT, CHAPTER 277
Aniline poisoning
Anthrax
Arsenical poisoning
Asbestosis
Barotrauma
Beryllium poisoning
Byssinosis
Cadmium poisoning
Carbon bisulphide poisoning
Carbon Dioxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Cataract
Chrome ulceration
Chronic benzene poisoning
Compressed air illness
Cyanide poisoning
Epitheliomatous ulceration
Glanders
Hydrogen sulphide poisoning
Lead poisoning
Leptospitosis
Liver angiosarcoma
Manganese poisoning
Mercurial poisonning
Mesothelioma
Nitrous fumes poisoning
Noise-induced deafness
Occupational skin diseases
Occupational asthma
Pesticide poisoning
Poisoning from halogen derivatives of hydrocarbon compounds
Radiation
Rengas wood poisoning
Repetitive strain disorders
Silicosis
Toxic anaemia
Toxic Hepatitis
Tuberculosis
